
Explanation of technical information
To ensure that you select wheels compatible with your vehicle and avoid any
unpleasant surprises
it is important to understand their technical
specifications. Take a moment to familiarize yourself with these specifications
and begin shopping for your new wheels with peace of mind.
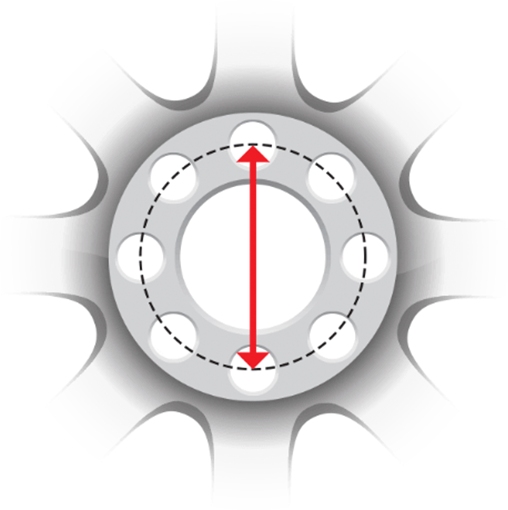
BOLT PATTERN
The bolt pattern is calculated using the number
of holes on the wheel and an imaginary circle passing through the center of the
wheel studs, representing its diameter in millimeters (mm). In the case of a
wheel with five (5) holes and a circle diameter of 114.3 mm, the bolt pattern
of this wheel is therefore 5x114.3. It is important to ensure that the bolt
pattern of your vehicle matches that of your wheels; otherwise, it will be impossible
to install your wheels.
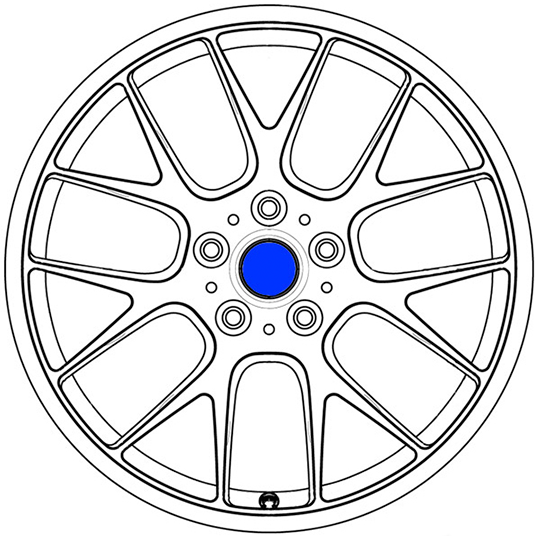
CENTRE BORE
The center bore is the central hole located in
the middle of your wheels. This allows for proper positioning of the wheel on
the vehicle's hub. It is important that the wheel's center bore diameter is
equal to or larger than the hub size of the vehicle. The center bore is
measured in millimeters (mm) using the diameter of this hole.

LUG CENTRIC
This type of centering is very common for steel
wheels but uncommon for alloy wheels. The principle is the same as hub
centering, except that this type of centering is done using the lug nuts. The
reason for this type of centering lies in the fact that it is impossible to use
centering rings with steel wheels.
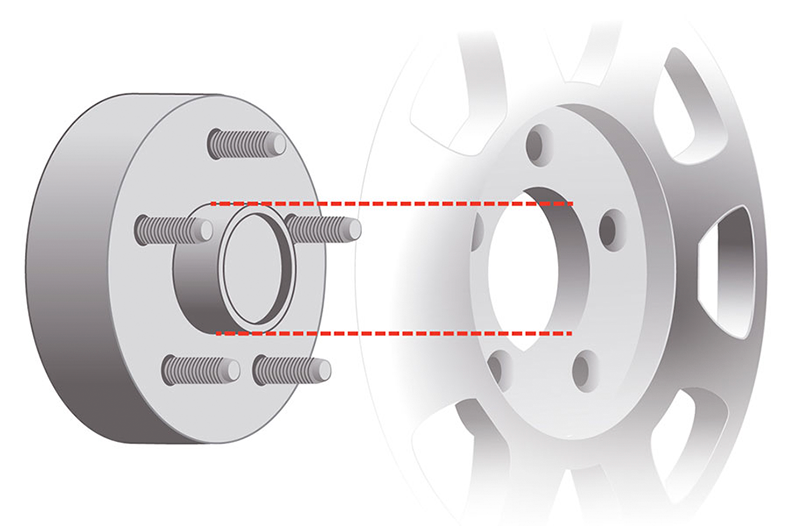
HUB CENTRIC
Hub centering is done using the central hole
located in the middle of the wheel. Once installed on the vehicle's hub, this
helps prevent possible vibrations. Most aftermarket wheels require the use of
centering rings, as they are designed with a larger hub to fit a greater number
of vehicles. These centering rings have an outer diameter corresponding to the
size of the wheel's hub diameter and an inner diameter corresponding to the
size of the vehicle's hub, ensuring a perfect fit no matter the vehicle on which
you install the wheels.
OFFSET
The offset is the measure of the distance between the centre of the wheel to the hub mounting point on the wheel.
There are 3 categories of offset:

A. ZERO OFFSET:
This is when the hub mounting point on the wheel is aligned with the middle of the wheel. This kind of offset is mostly used for older rear wheel drive cars or for pickup trucks with large fenders.

B. POSITIVE OFFSET
This is when the hub mounting point of the wheel is toward the outside or front of the wheel. This kind of offset is the norm for front wheel drive cars and most modern rear wheel drive cars.

C. NEGATIVE OFFSET
This is when the hub mounting point of the wheel is toward the inside or rear of the wheel. This kind of offset is mostly used for older rear wheel drive cars, lifted pickup trucks with fender extensions or sports cars with over fenders or fender flares. It is important to select a wheel with the correct offset range for your vehicle. Choosing a wrong offset can affect the handling of the vehicle.

